What is wafer dicing equipment?
Wafer dicing equipment, also known as wafer dicer, is a machine used in semiconductor device manufacturing to cut finished wafers into individual chips or dies without damaging them. A precise and accurate dicing process is crucial for separating chips while maintaining the integrity of their structures and embedded circuits. The wafer dicing machine is designed to perform precise and efficient wafer dicing while maintaining the chips' integrality.
 Figure: Wafer dicing equipment
Figure: Wafer dicing equipment
After dicing, the chips are packaged and tested to make them suitable for use in electronic products such as calculators, cell phones, and more.
Dicing technique and equipment:
The wafer dicing machine can use dicing techniques such as blade dicing, laser dicing, and plasma dicing.
Blade dicing equipment (Blade dicer): This machine utilizes a fine diamond-coated rotating blade (typically, 15,000 to 30,000 RPM) to mechanically slice through the wafer. The blade is mounted on a wafer dicing saw. The blade dicer features the following key components in addition to other supporting elements.
- Spindle: Rotates the blade at higher speeds.
- Blade: A diamond-coated blade to cut through predefined dicing lines on the wafer.
- Chuck: Used to safely hold the wafer in place during the dicing process.
- Coolant System: Cools the blade and wafer to prevent overheating and reduce dust.
The blade dicing method is ideal for cutting silicon wafers and is a widely used cost-effective method.
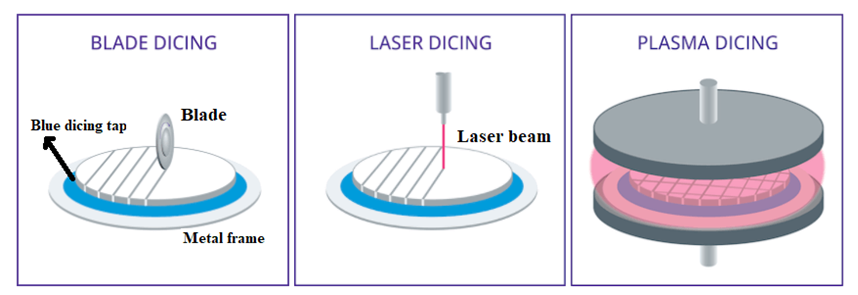 Figure: Various wafer dicing techniques
Figure: Various wafer dicing techniques
Laser dicing equipment (laser dicer): This machine uses laser technology to cut through the predefined dicing lines on the wafer. It is a non-contact process, avoiding mechanical stress on the wafer. The laser dicer features the following key components in addition to other supporting elements.
- Laser Source: Generating the laser beam for the wafer cutting.
- Optics System: Directing and focusing the laser beam onto the wafer to cut.
- Beam Delivery System: Used to control the movement and intensity of the laser beam.
- Chuck: Holds the wafer in place during laser dicing.
This dicing equipment can utilize various types of lasers, such as infrared (IR) lasers, ultraviolet (UV) lasers, and femtosecond lasers. They are ideal for dicing thicker wafer, thin, and fragile wafers, as well as for dicing densely packed advanced semiconductor wafers. This machine provides high precision and accuracy but is costlier than blade dicing.
Plasma equipment (plasma dicer): This equipment uses plasma, an ionized gas, to etch away material along predefined dicing lines to separate chips. It is a non-contact process, avoiding mechanical stress on the wafer. The key components of this machine include the following:
- Plasma Source: Used to generate the plasma for etching.
- Reaction Chamber: The wafer is placed inside the reaction chamber and exposed to the plasma.
- Chuck: Used to hold the wafer in the chamber during dicing.
- Gas Delivery System: Supplies the etching gases such as argon, oxygen, and CF₄,
The plasma dicing process begins with applying a mask on the wafer to define dicing lines. Then, the wafer is placed inside the reaction chamber, and the etching gas is supplied. An electric field is now applied to ionize the gas, creating plasma. The plasma contains reactive ions and radicals. These reactive ions and radicals interact with wafer material and etch away material in the exposed dicing areas defined by the mask. The plasma dicing technique can etch away the material on all the dicing lines simultaneously, providing higher yields.
The plasma dicer is ideal for cutting thin and fragile wafers, brittle wafers, as well as densely packed advanced semiconductor wafers. This machine provides high precision and accuracy but is costlier than blade dicing.
Wafer dicing equipment selection:
Wafer dicing equipment can be integrated into the production lines of the semiconductor manufacturing process. They are available in semi and fully-automatic features and can handle a wafer's diameter typically up to 300 mm. When selecting wafer dicing machine, consider factors such as wafer material properties, chip size and geometry, precision and accuracy, compatibility, efficiency, and cost.